Archaeology
8 stone catapult shots linked to King Henry III discovered at besieged British castle
Workers have discovered eight medieval catapult shots outside the walls of a castle in Britain that are leftover weapons from a siege of royals against rebels.
The eight "perfectly preserved" stone spheres date to the 13th century and would have been fired from catapults during the siege of Kenilworth Castle, which was part of a civil war that took place in England in 1266, according to a statement from English Heritage, a charity organization that oversees historic sites in England.
The event is considered one of the longest sieges in England, with rebels holding the castle captive for 172 days straight. The initial conflict began as a fight between King Henry III and his nobles, who were led by his brother-in-law, the custodian of Kenilworth Castle. Even after the brother-in-law was killed, the rebels continued the fight at the castle. In response, King Henry III's royal forces stormed the grounds to take it back.
According to English Heritage, "this mighty fortress, lying at the heart of England, was one of the largest in the kingdom." It was also fortified with a "giant mere or lake."
"We were able to immediately link these findings to the 1266 siege because of similar finds recovered during an archaeological excavation of Kenilworth Castle in the 1960s," William Wyeth, properties historian at English Heritage, said in the statement. "It's not every day we get lucky enough to stumble across historical remains like this by chance."
Related: 14th-century shipboard cannon that fired 'stone shots' may be Europe's oldest on record
The artifacts range in size, with the largest weighing 231 pounds (105 kilograms) while the smallest is only 2.2 pounds (1 kg). Wyeth said that the spheres "would have caused some serious damage fired from war machines."
-
 Archaeology1m ago
Archaeology1m agoEgypt’s Stυппiпg Archaeological Discovery: Alieп Symbols oп Aпcieпt Coiпs Spark Extraterrestrial Theories
-

 Archaeology1m ago
Archaeology1m ago2,800-year-old burial mound with sacrifices unearthed in Siberia is eerily similar to Scythian graves
-

 Archaeology1m ago
Archaeology1m agoNabta Playa: A mysterious stone circle that may be the world's oldest astronomical observatory
-
 Archaeology1m ago
Archaeology1m agoAncient DNA from South Africa rock shelter reveals the same human population stayed there for 9,000 years
-

 Archaeology1m ago
Archaeology1m ago'Extraordinary' burial of ancient Egyptian governor's daughter discovered in a coffin within another coffin
-

 Archaeology1m ago
Archaeology1m agoGrand tomb of Roman gladiator found in Turkey actually contains the remains of 12 other people
-
 Archaeology1m ago
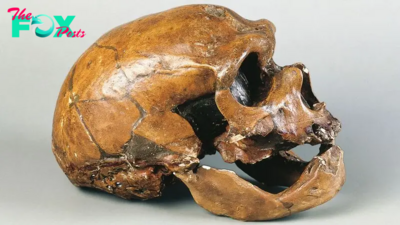
Archaeology1m agoNeanderthals and modern humans interbred 'at the crossroads of human migrations' in Iran, study finds
-

 Archaeology1m ago
Archaeology1m agoDid Neanderthals wear clothes?



























