Science
Hranice Abyss: The deepest freshwater cave on Earth and a conduit to a 'fossil' sinkhole
Name: Hranice Abyss
Location: Hranice, Czech Republic
Coordinates: 49.53214473576795, 17.750610529720298
Why it's incredible: The cave is so deep, the world's tallest building could fit inside it.
The Hranice Abyss — or "Hranická propast," in Czech — is the deepest known freshwater cave in the world. Geologists think it could extend more than half a mile (1 kilometer) below Earth's surface, which is more than twice as deep as the world's next-deepest freshwater cave.
The Hranice Abyss challenges a long-held scientific belief that deep caves open from the bottom up, with warm, acidic groundwater rising and dissolving the bedrock. According to a 2020 study in the Journal of Geophysical Research: Earth Surface, that's not how the abyss formed. Instead, evidence shows water carved the cave from the top down.
Related: Deepest blue hole in the world discovered, with hidden caves and tunnels believed to be inside
Scientists first described the Hranice Abyss in 2016, after conducting numerous dives inside the cave. Researchers then deployed a remotely operated vehicle (ROV) to explore the corners that divers couldn't reach and measured a maximum depth of 1,553 feet (473.5 m), according to the 2020 study.
This established the Hranice Abyss as the deepest freshwater cave in the world, beating Italy's Pozzo del Merro, which descends 1,286 feet (392 m) below the surface. However, the recorded depth was constrained by the length of a fiber-optic communication cable attached to the ROV.
The 2020 study used gravity and seismic imaging methods to investigate the true extent of the Hranice Abyss. The results suggested the cave was more than twice as deep as the ROV had previously gone — and deep enough to fit the world's tallest building, the Burj Khalifa, which stands 2,717 feet (828 m) tall.
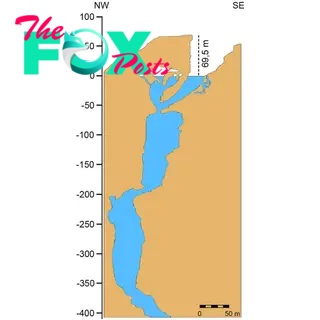
The opening of the Hranice Abyss is an inclined cavity with a small lake at the bottom, according to the latest study. The underwater portion of the cave is an irregular, vertical cylinder ranging from 30 to 100 feet (10 to 30 m) in diameter. Water temperatures in the cave vary between 58 and 66 degrees Fahrenheit (14.5 to 18.8 degrees Celsius) depending on the time of year.
-

 Science10h ago
Science10h agoWhy Risky Wildfire Zones Have Been Increasing Around the World
-

 Science16h ago
Science16h agoIt’s Time to Redefine What a Megafire Is in the Climate Change Era
-

 Science1d ago
Science1d ago4 Astronauts Return to Earth After Being Delayed by Boeing’s Capsule Trouble and Hurricane Milton
-

 Science2d ago
Science2d agoThe Elegance and Awkwardness of NASA’s New Moon Suit, Designed by Axiom and Prada
-

 Science1w ago
Science1w agoSpaceX Launches Its Mega Starship Rocket. This Time, Mechanical Arms Catch It at Landing
-

 Science3w ago
Science3w agoYou Won’t Want to Miss October’s Rare Comet Sighting. Here’s How and When You Can See It
-

 Science1m ago
Science1m agoA New Spacecraft Could Help Determine if There’s Life on a Moon of Jupiter
-

 Science1m ago
Science1m agoWe Can Thank Deep-Space Asteroids for Helping Start Life on Earth



























