Health
What's the difference between gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria?
Most species of bacteria can be broadly divided into two groups, known as gram-positive and gram-negative. These categories reflect big differences in the microbes' biology, and they also dictate how doctors treat bacterial infections.
But what are the differences between gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria?
The names themselves date back to 1884, when Danish bacteriologist Hans Christian Gram developed a staining procedure to view bacteria under the microscope. First, he applied a dye, called gentian violet, which penetrates both the protective wall and membrane of bacteria, thus staining the material inside. Then, he added the mineral iodine, which formed a complex with the dye that wouldn't break down in water, thus "fixing" the stain in place.
After being washed with alcohol, some bacteria remained blue or purple, while others did not retain the stain. The first group was dubbed "gram-positive," while the latter was designated "gram-negative."
Related: Dangerous 'superbugs' are a growing threat, and antibiotics can't stop their rise. What can?
Gram's stain experiment pointed toward some sort of difference in the structures of various bacterial cells. However, it was not until the early 1950s that scientists started to understand the differences in the chemical composition of bacterial cell walls that makes a difference in the staining.
Differences between gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria
All bacteria have a cell wall composed of mesh-like strands of a big molecule called peptidoglycan, which surrounds the cell membrane. A cell wall provides the bacterial cell sturdiness and helps maintain its shape and internal pressure. However, there are some key differences between the two classes of bacteria.
-

 Health5h ago
Health5h agoThe Best Way to Treat Insomnia
-
 Health22h ago
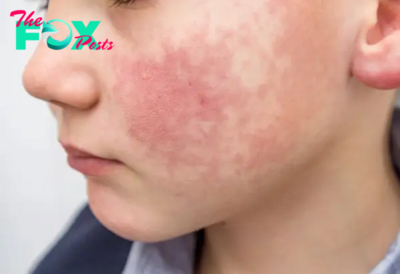
Health22h agoWhat to Know About Parvovirus B19, a Respiratory Virus on the Rise
-
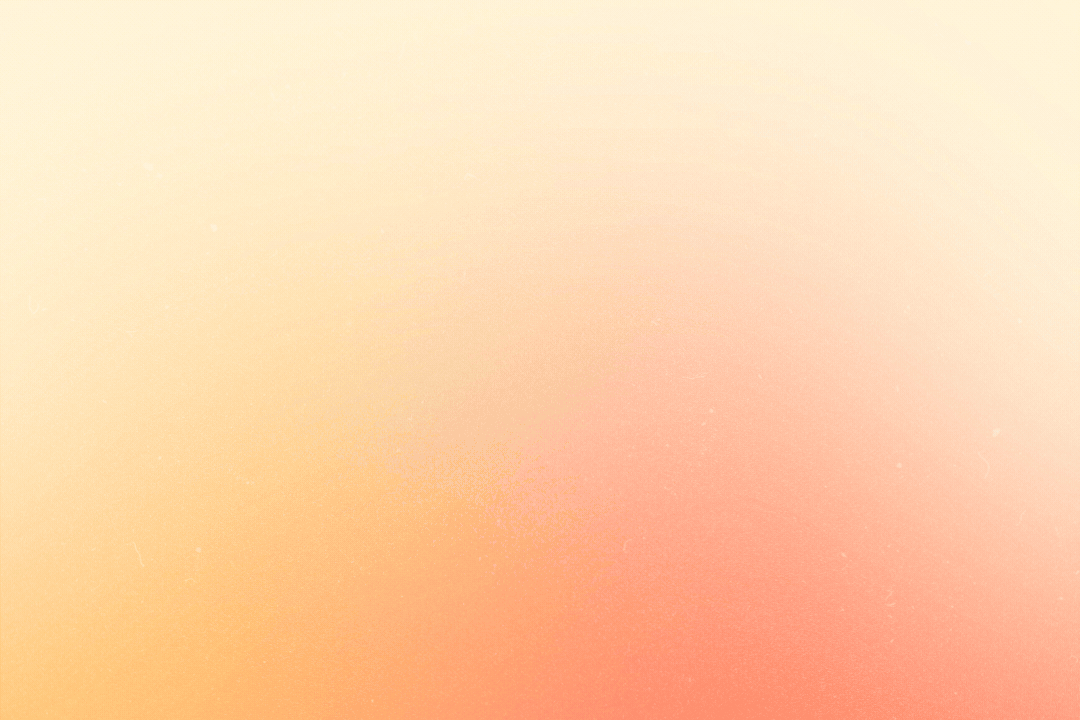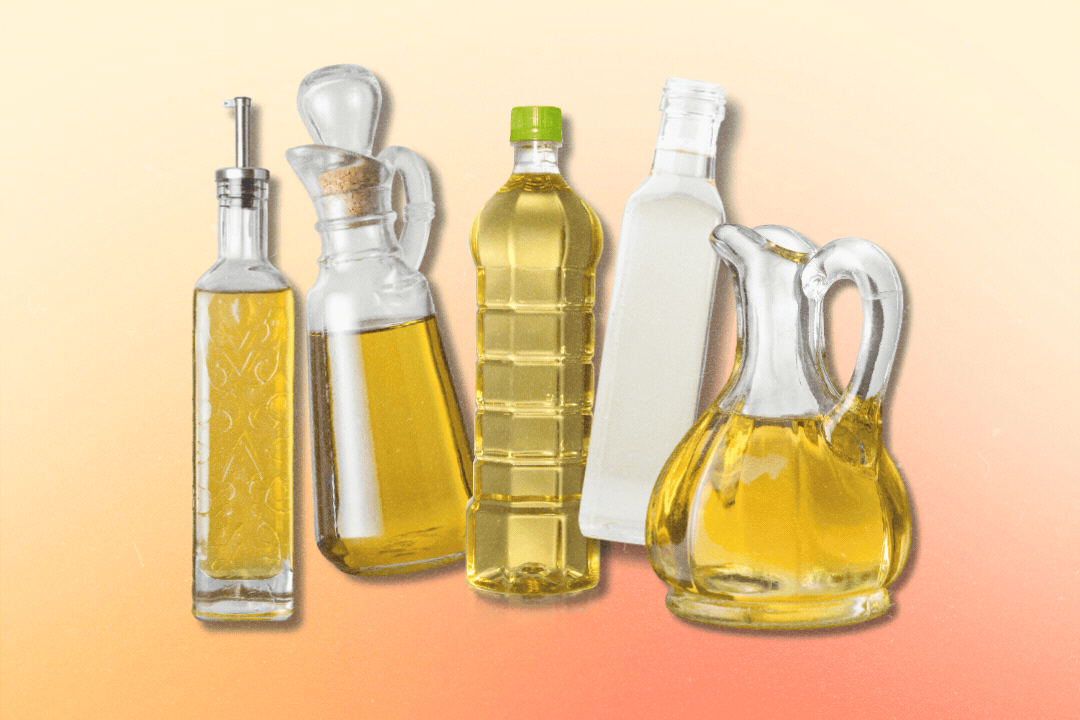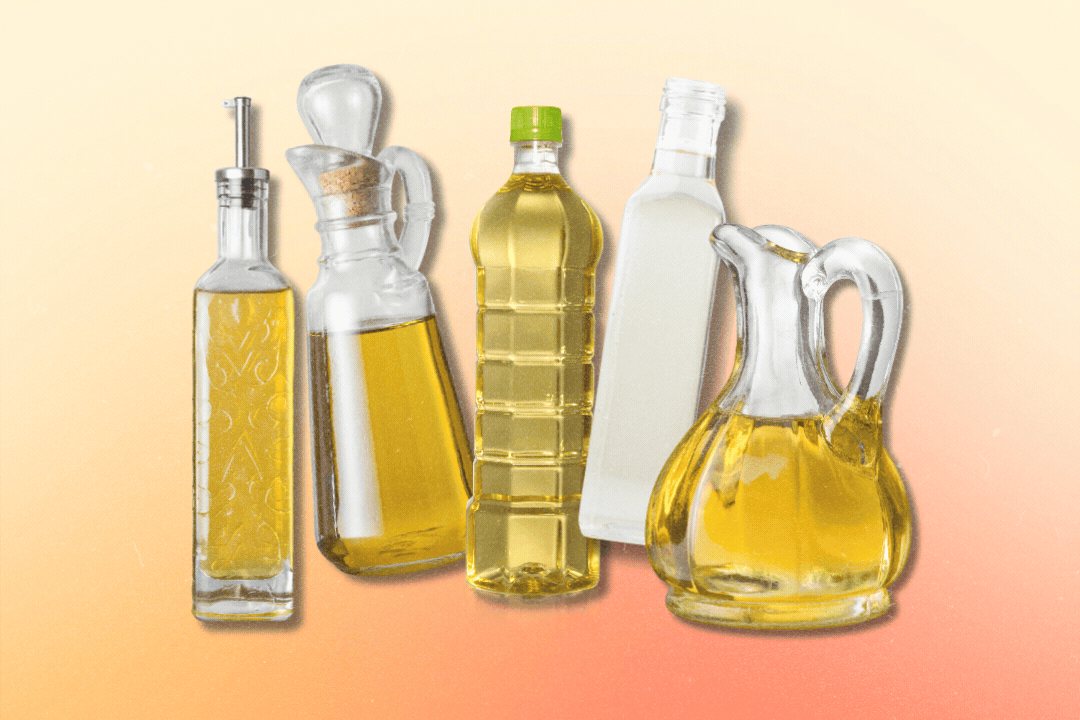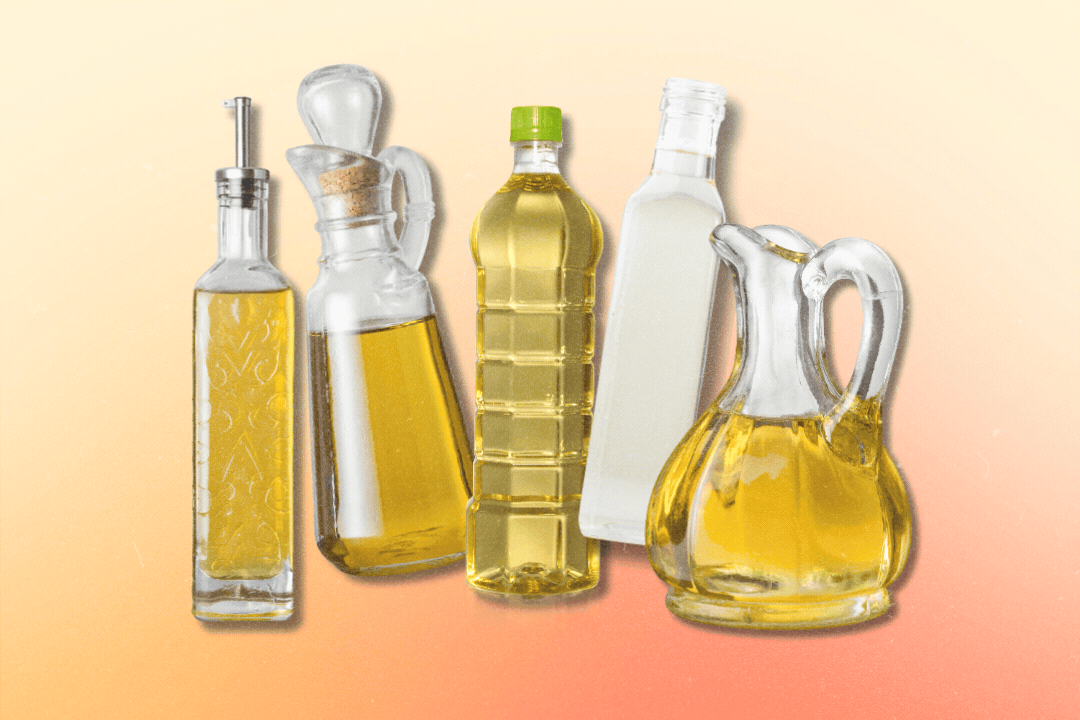
 Health22h ago
Health22h ago6 Health Myths About Oils
-

 Health23h ago
Health23h ago'Banana apocalypse' could be averted thanks to genetic breakthrough
-
 Health1d ago
Health1d agoWhat to Expect at a Colonoscopy
-

 Health1d ago
Health1d agoHuman aging accelerates dramatically at age 44 and 60
-

 Health1d ago
Health1d agoBiden administration’s negotiated price cuts for 10 common prescription drugs likely to save Medicare billions, beginning in 2026
-

 Health3d ago
Health3d agoScientists finally explain MIS-C, the rare post-COVID sydrome seen in kids



















