Health
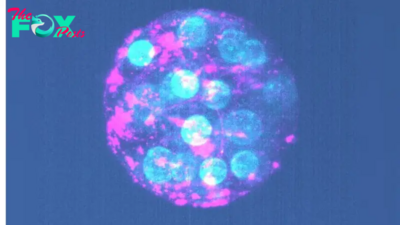
Newborns are colonized with antibiotic resistant bacteria
Sepsis occurs when one's immune system has an extreme response to an infection. It’s a life-threatening condition: globally, it accounts for about 11 million deaths — 20% of all deaths per year.
And it doesn't just affect adults. In 2020, 2.4 million newborn babies died of sepsis in the first month of their lives. Most of these deaths happened in sub-Saharan Africa.
The main treatment for sepsis is antibiotics. However, the overuse and misuse of antibiotics in human medicine and agriculture has led to antimicrobial resistance — a process in which bacteria, fungi and parasites have developed the ability to resist the action of medicines.
The World Health Organization describes antimicrobial resistance as one of the top global public health and development threats.
This growing resistance is due to the overuse and misuse of antibiotics in both human medicine and in farming. They're used in large quantities to grow crops and in animal feeds to treat and reduce the risk of infection in livestock.
It has been forecast that, by 2050, more people will die from antimicrobial resistance than both cancer and diabetes combined.
RELATED: Scientists have found a secret 'switch' that lets bacteria resist antibiotics — and it's been evading lab tests for decades
-
 Health7h ago
Health7h agoThe Surprising Benefits of Talking Out Loud to Yourself
-
 Health8h ago
Health8h agoDoctor’s bills often come with sticker shock for patients − but health insurance could be reinvented to provide costs upfront
-

 Health14h ago
Health14h agoHow Colorado is trying to make the High Line Canal a place for everyone — not just the wealthy
-

 Health23h ago
Health23h agoWhat an HPV Diagnosis Really Means
-

 Health1d ago
Health1d agoThere’s an E. Coli Outbreak in Organic Carrots
-

 Health2d ago
Health2d agoCOVID-19’s Surprising Effect on Cancer
-

 Health2d ago
Health2d agoColorado’s pioneering psychedelic program gets final tweaks as state plans to launch next year
-

 Health3d ago
Health3d agoWhat to Know About How Lupus Affects Weight