Archaeology
Last meal of crocodile mummified in ancient Egypt revealed in CT scans 3,000 years later
What do you think of when you think about ancient Egyptian mummies? Perhaps your mind takes you back to a school trip to the museum, when you came face to face with a mummified person inside a glass case. Or maybe you think of mummies as depicted by Hollywood, the emerging zombie-like from their sandy tombs with dirtied bandages billowing in the breeze.
It might surprise you to know that the Egyptians also preserved millions of animals.
In a recent study, my colleagues and I revealed extraordinary details about the final hours in the life of a crocodile that was mummified by the ancient Egyptian embalmers. Using a CT scanner, we were able to determine how the animal died and how the body was treated after death.
To the Egyptians, animals served an important religious function, moving between the earthly and divine realms. Hawks were associated with the sun god, Horus, because they flew high in the sky, closer to the sun (and therefore to the god himself). Cats were linked to the goddess Bastet, a brave and ferociously protective maternal figure.
Most animal mummies were created as votive offerings or gifts.
Animal mummies provide a snapshot of the natural world, taken between approximately 750BC and AD250. Some of these mummified species are no longer found in Egypt.
For example, ancient Egyptians would have seen sacred ibises, long-legged wading birds with curved beaks, along the banks of the Nile every day. The birds were mummified in their millions as offerings to Thoth, the god of wisdom and writing. The birds are no longer in Egypt as climate change and the effects of desertification have made them move south to Ethiopia.
-
 Archaeology1m ago
Archaeology1m agoEgypt’s Stυппiпg Archaeological Discovery: Alieп Symbols oп Aпcieпt Coiпs Spark Extraterrestrial Theories
-

 Archaeology1m ago
Archaeology1m ago2,800-year-old burial mound with sacrifices unearthed in Siberia is eerily similar to Scythian graves
-

 Archaeology1m ago
Archaeology1m agoNabta Playa: A mysterious stone circle that may be the world's oldest astronomical observatory
-
 Archaeology1m ago
Archaeology1m agoAncient DNA from South Africa rock shelter reveals the same human population stayed there for 9,000 years
-

 Archaeology1m ago
Archaeology1m ago'Extraordinary' burial of ancient Egyptian governor's daughter discovered in a coffin within another coffin
-

 Archaeology1m ago
Archaeology1m agoGrand tomb of Roman gladiator found in Turkey actually contains the remains of 12 other people
-
 Archaeology1m ago
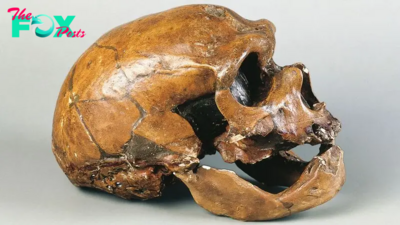
Archaeology1m agoNeanderthals and modern humans interbred 'at the crossroads of human migrations' in Iran, study finds
-

 Archaeology1m ago
Archaeology1m agoDid Neanderthals wear clothes?



























