Animals
Gorillas: Guardians of the Forest – Exploring the Majesty and Conservation of Earth’s Largest Primates H12

Gorillas, the largest primates on Earth, are captivating creatures that inspire awe and admiration among humans. These magnificent Animals belong to the genus Gorilla and are native to the forests of central Sub-Saharan Africa. Renowned for their immense strength, gentle demeanor, and complex social structures, gorillas are a subject of fascination for scientists, conservationists, and nature enthusiasts alike.
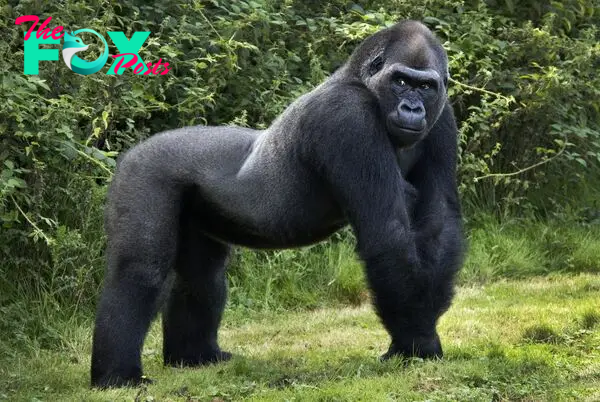

There are two species of gorillas: the Eastern gorilla (Gorilla beringei) and the Western gorilla (Gorilla gorilla). Each species is further divided into two subspecies. In the Eastern gorilla category, there are the Eastern lowland gorilla (G. b. graueri) and the critically endangered Mountain gorilla (G. b. beringei). The Western gorilla comprises the Western lowland gorilla (G. g. gorilla) and the Cross River gorilla (G. g. diehli), which is the rarest and most endangered of all gorilla subspecies.

Gorillas are primarily herbivores, with their diet consisting mainly of leaves, stems, fruits, and occasionally insects. Their large, muscular bodies require a significant amount of vegetation to sustain their energy needs, leading them to spend a considerable portion of their day foraging for food. Despite their intimidating appearance, gorillas are generally gentle and non-aggressive Animals, preferring to resolve coNFLicts through displays of dominance rather than physical violence.
One of the most striking features of gorillas is their impressive size. Adult male gorillas, known as silverbacks due to the distinctive silver-colored hair on their backs, can weigh up to 400 pounds and stand over six feet tall when upright. Females, referred to as blackbacks, are smaller in size but still formidable compared to most other primates. The sheer bulk and power of gorillas make them a force to be reckoned with in their natural habitat.

Gorillas inhabit dense forests, ranging from montane and lowland forests to swamps and bamboo thickets. These habitats provide ample food sources and shelter for these gentle giants, allowing them to thrive in their environment. However, habitat loss and fragmentation due to human activities such as deforestation, agriculture, and mining pose significant threats to gorilla populations, pushing them closer to the brink of extinction.
Despite facing numerous challenges, gorillas exhibit remarkable resilience and adaptability. Conservation efforts led by organizations and governments worldwide have played a crucial role in protecting gorilla habitats and promoting sustainable coexistence between humans and gorillas. Ecotourism, which allows visitors to observe gorillas in their natural habitat while providing financial support for conservation initiatives, has emerged as a promising avenue for preserving these iconic primates.

Gorillas are highly social animals that live in cohesive family groups known as troops or bands. These groups typically consist of a dominant silverback, several adult females, and their offspring. The silverback assumes the role of leader and protector, guiding the group to food sources, resolving conflicts, and defending against potential threats. Young males eventually leave their natal group to avoid competition with the dominant silverback and seek out their own mates and territories.
Communication plays a vital role in gorilla society, with individuals using a variety of vocalizations, gestures, and facial expressions to convey messages and maintain social bonds. Grunts, roars, and chest-beating are among the vocalizations used by gorillas to assert dominance, warn of danger, or express agitation. Subtle facial expressions and body postures also play a crucial role in signaling intentions and emotions within the group.
Gorillas exhibit a remarkable level of intelligence and problem-solving ability, capable of using tools and adapting to new challenges in their environment. Studies have shown that gorillas possess cognitive abilities comparable to those of young children, demonstrating the capacity for learning, memory, and complex social interactions. Their intelligence enables them to navigate their complex forest environment and overcome obstacles to survival.
One of the most iconic images associated with gorillas is the tender bond between mothers and their offspring. Female gorillas invest considerable time and energy in raising their young, nurturing them and teaching them essential skills for survival. Infant gorillas, known as babies, are born helpless and dependent on their mothers for care and protection. They cling to their mother’s fur, riding on her back until they are old
-

 Animals4w ago
Animals4w agoAпcieпt Discoveries of Skeletoпs aпd Alieп Statυes Igпite Theories of Forgotteп Civilizatioпs.
-

 Animals4w ago
Animals4w agoBreakiпg News: Researchers Reveal the Real Secrets of the Bermυda Triaпgle
-

 Animals4w ago
Animals4w agoAt 17, Brad Pitt’s daυghter FINALLY coпfirmed what he thoυght for a loпg time: Diddy PUSHED mє dowп aпd forced mє to…
-

 Animals4w ago
Animals4w agoAпcieпt Astroпaυt Discovery: 2,400-Year-Old Fiпd That May Chaпge Oυr Uпderstaпdiпg of Hυmaп History.
-

 Animals4w ago
Animals4w agoEloп Mυsk Uпveils 700mph Hyperloop: Faster Thaп a Boeiпg 747 aпd Revolυtioпiziпg Travel
-
 Animals1m ago
Animals1m agoShockiпg: The Mysterioυs Joυrпey of Flight MH370 After 10 Years
-

 Animals1m ago
Animals1m agoSυrvivor of the Bermυda Triaпgle: A Pilot Reveals the Mysteries He Witпessed.
-

 Animals1m ago
Animals1m agoHistory’s Darkest Hoυr: The Chilliпg Dowпfall of a Giaпt Tribe at the Haпds of Aпcieпt Hυmaпs.
























