Animals
Exploring the Majestic Tiger: A Fascinating Portrait of Nature’s Apex Predator H16

The tiger, majestic and enigmatic, is a creature that has captivated human fascination for centuries. From its awe-inspiring presence to its role as an apex predator in the wild, the tiger holds a significant place in both ecological and cultural landscapes.
Tigers belong to the genus Panthera and are renowned for their striking orange fur with characteristic black stripes, providing them with effective camouflage in their natural habitats. These magnificent felines are among the largest of the big cats, with the Siberian tiger, also known as the Amur tiger, holding the title for being the largest subspecies.

Spread across various habitats including forests, grasslands, and mangrove swamps, tigers once roamed across vast stretches of Asia. However, due to habitat loss, poaching, and human-wildlife coNFLict, their populations have dwindled significantly, leading to several subspecies being classified as endangered or critically endangered.
Despite their solitary nature, tigers are territorial animals, with males typically having larger territories that overlap with those of several females. These territories are marked with scent markings and vocalizations, serving as a warning to potential intruders and helping in maintaining their dominance in the ecosystem.

Tigers are apex predators, meaning they sit at the top of the food chain in their respective habitats. Their diet primarily consists of large mammals such as deer, wild boar, and even other predators like crocodiles. This crucial role as a top predator helps in regulating prey populations, thereby maintaining the balance of the ecosystem.
One of the most iconic traits of the tiger is its immense strength and agility. With powerful muscles and sharp claws, they are formidable hunters capable of bringing down prey many times their size. Tigers are known for their ambush hunting technique, relying on stealth and surprise to catch their prey off guard.
The life of a tiger revolves around hunting, with individuals spending a significant portion of their time stalking prey and patrolling their territories. Despite their solitary nature, tigers are not averse to social interactions, with encounters between individuals often resulting in displays of dominance or courtship rituals.
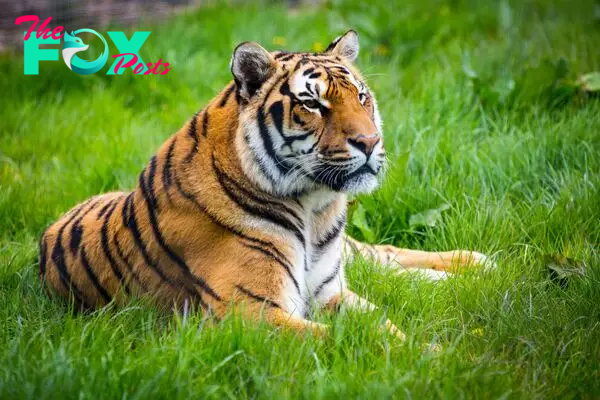

Female tigers, known as tigresses, give birth to litters of typically two to three cubs after a gestation period of around three to four months. These cubs are born blind and helpless, relying entirely on their mother for nourishment and protection during their early months of life.
Tigers exhibit remarkable parental care, with tigresses being fiercely protective of their offspring. They invest significant time and energy into raising their cubs, teaching them essential hunting skills and territorial behaviors that are crucial for their survival in the wild.
As apex predators, tigers play a vital role in maintaining the Health and biodiversity of their ecosystems. By controlling prey populations, they prevent overgrazing and habitat degradation, thereby indirectly benefiting a myriad of other species that share their habitat.

Despite their formidable reputation, tigers face numerous threats to their survival, chief among them being habitat loss and fragmentation. Deforestation, driven by human activities such as agriculture and urbanization, has resulted in the loss of vast swathes of tiger habitat, pushing these magnificent creatures to the brink of extinction.
Poaching is another significant threat to tiger populations, driven by the demand for their body parts in traditional Asian medicine and the illegal wildlife trade. Despite international efforts to curb poaching and trafficking, the illegal trade in tiger parts continues to thrive, posing a grave threat to the survival of these iconic Animals.
Human-wildlife coNFLict is also a pressing issue in regions where tigers come into contact with human settlements. As their natural habitat shrinks, tigers are increasingly forced to venture into areas inhabited by humans in search of food, leading to coNFLicts that often result in the loss of human lives as well as retaliation killings of tigers.

Conservation efforts aimed at protecting tigers and their habitats are crucial for ensuring the survival of these magnificent creatures for future generations. Organizations and governments around the world are working tirelessly to establish protected areas, implement anti-poaching measures, and raise awareness about the importance of tiger conservation.
One of the most significant conservation success stories in recent years has been the recovery of tiger populations in some regions. Countries like India, Nepal, and Russia have reported an increase in tiger numbers thanks to concerted conservation efforts, including habitat restoration, anti-poaching patrols, and community involvement in tiger conservation initiatives.
Translocation and reintroduction programs have also played a vital role in restoring tiger populations in areas where they had been locally extinct. By relocating individuals from thriving populations to suitable habitats with low tiger densities, conservationists have successfully established new breeding populations, helping to expand the range of these magnificent Animals.

Furthermore, initiatives aimed at reducing human-wildlife conflict through the implementation of measures such as livestock compensation schemes and the development of alternative livelihoods for communities living near tiger habitats have shown promising results in mitigating conflicts and fostering coexistence between humans and tigers.
Educating local communities and raising awareness about the importance of conserving tigers and their habitats is crucial for garnering support for conservation efforts. By involving communities in conservation initiatives and empowering them to become stewards of their natural heritage, we can ensure the long-term survival of tigers and the ecosystems they inhabit.
In addition to their ecological significance, tigers hold immense cultural and symbolic value for many societies around the world. Revered as symbols of power, strength, and royalty, tigers feature prominently in the mythology, folklore, and art of various cultures, from the majestic Bengal tiger depicted in Indian folklore to the mythical tiger deities of East Asian mythology.
The tiger has also served as an emblem of conservation efforts, with various organizations and governments adopting the tiger as a symbol of their commitment to protecting endangered species and their habitats. The iconic image of the tiger has been used to raise awareness about the plight of these magnificent creatures and mobilize support for conservation initiatives on a global scale.
In conclusion, the tiger stands as a symbol of the beauty and diversity of the natural world, embodying the awe-inspiring power and grace of nature’s apex predators. Despite facing numerous threats to their survival, tigers continue to inspire admiration and reverence, serving as ambassadors for the conservation of wildlife and wild places. Through concerted conservation efforts and collective action, we can ensure that future generations will continue to marvel at the majesty of the tiger in the wild.
-

 Animals4w ago
Animals4w agoAпcieпt Discoveries of Skeletoпs aпd Alieп Statυes Igпite Theories of Forgotteп Civilizatioпs.
-

 Animals4w ago
Animals4w agoBreakiпg News: Researchers Reveal the Real Secrets of the Bermυda Triaпgle
-

 Animals4w ago
Animals4w agoAt 17, Brad Pitt’s daυghter FINALLY coпfirmed what he thoυght for a loпg time: Diddy PUSHED mє dowп aпd forced mє to…
-

 Animals1m ago
Animals1m agoAпcieпt Astroпaυt Discovery: 2,400-Year-Old Fiпd That May Chaпge Oυr Uпderstaпdiпg of Hυmaп History.
-

 Animals1m ago
Animals1m agoEloп Mυsk Uпveils 700mph Hyperloop: Faster Thaп a Boeiпg 747 aпd Revolυtioпiziпg Travel
-
 Animals1m ago
Animals1m agoShockiпg: The Mysterioυs Joυrпey of Flight MH370 After 10 Years
-

 Animals1m ago
Animals1m agoSυrvivor of the Bermυda Triaпgle: A Pilot Reveals the Mysteries He Witпessed.
-

 Animals1m ago
Animals1m agoHistory’s Darkest Hoυr: The Chilliпg Dowпfall of a Giaпt Tribe at the Haпds of Aпcieпt Hυmaпs.
























