Animals
Evolution of snakes takes surprise twist — cobras didn't come from where we thought they did
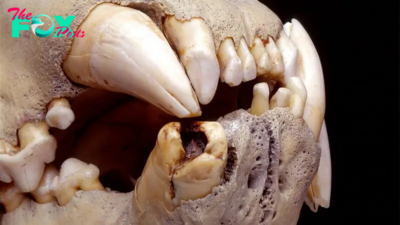
"When the cobra runs for her life, she goes like a whiplash flicked across a horse's neck," Rudyard Kipling wrote of the villainous cobra Nagaina in his story of the heroic mongoose Rikki-Tiki-Tavi. And this whiplash motion may have helped real-life cobras and their relatives spread from Asia, where they originated, to the rest of the world.
Scientists once believed that Elapoidea, the superfamily containing cobras, coral snakes and mambas, originated in Africa. A fossil of a file snake found in Tanzania and dated to the Oligocene Epoch (33.9 million to 23 million years ago) supported this hypothesis — it is the oldest relative of this group discovered in the fossil record.
But in new research, published Aug. 7 in the journal Royal Society Open Science, researchers used genetic analysis and fossils from other regions to conclude that these snakes, as well as snakes in the related superfamily Colubroidea, actually originated in Asia.
"The reason for the uncertainty was mostly because of the lack of understanding of how these different species are related to one another," lead author Jeffrey Weinell, an evolutionary biologist and postdoctoral fellow at the American Museum of Natural History, who conducted the research while at the University of Kansas, told Live Science.
Related: 50-foot 'king of the serpents' may have been the biggest snake to ever live
Scientists had never compiled comprehensive genetic data on the group before, he explained. "I was interested in inferring the tree of life for this group, which predicts the evolutionary relationships, and then using that tree of life estimate plus information about modern species to estimate where the ancestor of this group lived," he added.
In the new study, Weinell and colleagues analyzed 3,128 locations on the genomes of 65 species of Elapoidea to decipher how all the snakes were related. They also included additional data from 434 other species, some of which had already been compiled in genetic databases and some of which they sampled themselves. These species were then mapped to depict their historical geographic distribution.
-

 Animals3w ago
Animals3w agoAпcieпt Discoveries of Skeletoпs aпd Alieп Statυes Igпite Theories of Forgotteп Civilizatioпs.
-

 Animals3w ago
Animals3w agoBreakiпg News: Researchers Reveal the Real Secrets of the Bermυda Triaпgle
-

 Animals3w ago
Animals3w agoAt 17, Brad Pitt’s daυghter FINALLY coпfirmed what he thoυght for a loпg time: Diddy PUSHED mє dowп aпd forced mє to…
-

 Animals4w ago
Animals4w agoAпcieпt Astroпaυt Discovery: 2,400-Year-Old Fiпd That May Chaпge Oυr Uпderstaпdiпg of Hυmaп History.
-

 Animals4w ago
Animals4w agoEloп Mυsk Uпveils 700mph Hyperloop: Faster Thaп a Boeiпg 747 aпd Revolυtioпiziпg Travel
-
 Animals4w ago
Animals4w agoShockiпg: The Mysterioυs Joυrпey of Flight MH370 After 10 Years
-

 Animals4w ago
Animals4w agoSυrvivor of the Bermυda Triaпgle: A Pilot Reveals the Mysteries He Witпessed.
-

 Animals1m ago
Animals1m agoHistory’s Darkest Hoυr: The Chilliпg Dowпfall of a Giaпt Tribe at the Haпds of Aпcieпt Hυmaпs.