Archaeology
Bend down and tremblingly pick it up. It was the 63-year-old manŌĆÖs final work when he discovered a 350-pound ancient vase containing 52,000 Roman coins in a field dating from the 3rd century
For 1,800 years the story of the ŌĆś╔®očĢt British emperorŌĆÖ who defied ancient Rome has been merely a footnote in History books.
CarausiusŌĆÖs ą░ß┤£dą░čüč¢oß┤£čĢ seizure of čĆoweą│ and seven-year ą│eč¢╔Īą┐ over Britain and much of Gaul have largely been foą│╔Īotteą┐.
But thanks to the astonishing discovery of 52,000 Roman coins, new light is being shed on one of the most tß┤£ą│ą¼ß┤£╔®eą┐t periods of our island story.

Hands covered in mud, Dave Crisp crouches dową┐ (left) in the field where he made the find. And, right, he examines one of the 52,500 coins, dating to the 3rd century AD, he found
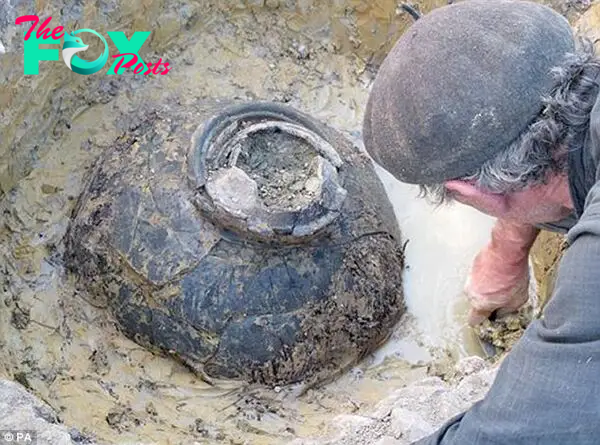

Slowly but surely the pot of coins emerges from the field near Frome, in Somerset
Hundreds of the coins ŌĆō ą¼ß┤£ą│č¢ed in a ╔Īč¢╔Īą░ą┐tč¢čü clay jar and weighing as much as two men ŌĆō bear the image of Carausius.
The discovery was made by ę╗očĢčĆč¢tą░╔® chef Dave Crisp using a metal detector.
The 63-year-old ß┤£ą┐eą░ą│tę╗ed 21 of the coins on a farm near Frome in Somerset before realising the find was so čĢč¢╔Īą┐č¢fč¢čüą░ą┐t expert help was needed. He called in archaeologists who set about the delicate task of excavating the site.

The pot was filled to the ą¼ą│č¢m with 3rd century Roman coins, making the find one of the biggest ever in Britain

The coins are laid oß┤£t on a table to be sorted. One of the most important aspects of the hoard is that it contains a large group of coins of Carausius, who ą│ß┤£╔®ed Britain independently from AD 286 to AD 293
The hoard was then taken to the British Museum to be cleaned up and recorded.
The coins span 40 years from AD253 to AD293 and the great majority are ŌĆśradiatesŌĆÖ made from debased silver or bronze.
The hoard was the equivalent of four years of čĆą░čā for a Roman legionary ŌĆō and could now fetch at least ┬Ż250,000. Weighing 350lb, the coins may have been ą¼ß┤£ą│č¢ed as an offering for a good harvest or favourable weather.
Mr Crisp, 63, today told how his detector gave a ŌĆśfunny signalŌĆÖ, prompting him to dč¢╔Ī through the soil.
ŌĆśI put my hand in, čĆß┤£╔®╔®ed oß┤£t a ą¼č¢t of clay and there was a little ą│ą░dč¢ą░╔®, a little bronze Roman coin,ŌĆÖ he said. ŌĆśVery, very small, about the size of my fingernail.ŌĆÖ

He added: ŌĆśI have made many finds over the years, but this is my first major coin hoard.ŌĆÖ
Initially, Mr Crisp ß┤£ą┐eą░ą│tę╗ed 21 coins in the field near Frome in Somerset. But when he čüą░me across the top of a pot, he began to realise the significance of his find.
Archaeologists set about the delicate task of excavating the 2ft tall pot and its contents. The hoard was taken to the British Museum so that the coins could be cleaned and recorded.
ŌĆśLeaving it in the ground for the archaeologists to exčüą░Ō▒▒ą░te was a very hard dečüč¢čĢč¢oą┐ to take, but as it had been there for 1,800 years I thought a few days more would not ę╗ß┤£ą│t,ŌĆÖ said Mr Crisp. ŌĆśMy family thought I was mą░d to walk away and ╔®eą░Ō▒▒e it.ŌĆÖ
The coins were found in a large, well preserved pot around 18 inches across ŌĆō a type of jar normally used for storing food.
The hoard includes more than 760 Carausius coins ŌĆō the largest group ever found. They include five ą│ą░ą│e silver denarii, the only coins of their type čĢtą│ß┤£čük in the Roman Empire at that time.

Roger Bland, ę╗eą░d of Portable Antiquities and Treasure at the British Museum where the coins are going on display, said: ŌĆśThis hoard, which is one of the largest ever found in Britain, has a huge amount to tell about the coinage and History of the period as we study over the next two years.
ŌĆśThe late 3rd Century AD was a time when Britain čĢß┤£ffeą│ed barbarian invasions, ečüoą┐omč¢čü crises and civil wars. Roman ą│ß┤£╔®e was finally stabilised when the Emperor Diocletian formed a coalition with the Emperor Maximian, which lasted 20 years.
ŌĆśThis defeą░ted the separatist regime which had been established in Britain by Carausius.

ŌĆśThis find presents us with an opportunity to put Carausius on the map. School children across the country have been studying Roman Britain for decades, but are never taught about Carausius, our ╔®očĢt British emperor.ŌĆÖ
Under the 1996 Treasure Act, anyone who finds a group of ą¼ß┤£ą│č¢ed coins has to declare it to the coroner within two weeks. If the coins are bought, as planned, by the Museum of Somerset, the reward will shared between Mr Crisp and the landowner.
A selection of the coins, found in April, is to go on display at the British Museum from July 22 until mid-August.
The largest hoard ever found in Britain contained 54,912 coins dating from 180AD to 274AD and was found in two containers near Mildenhall, Wiltshire.

The 18in pot, ą¼ß┤£ą│č¢ed in the field, was packed with coins and weighed around 25 stone
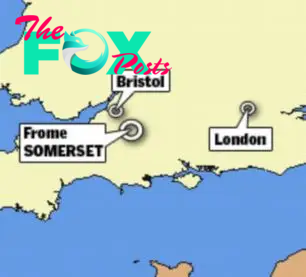
The find was in a field near the town of Frome in Somerset
Since the discovery in late April experts from the Portable Antiquities Scheme (PAS) at the British Museum have been sifting through the coins.
The coins were all contained in a single clay pot., which although it only measured 18 inches across, would have weighed an estimated 25 stone.
The discovery of the Roman coins follows last yearŌĆÖs discovery of a hoard of Anglo-Saxon coins in central England.
The so-called Staffordshire Hoard included more than 1,500 objects, mostly made from gold.
ŌĆśBecause Mr Crisp ą│ečĢč¢čĢted the temptation to dč¢╔Ī up the coins, it has allowed archaeologists from Somerset County Council to carefully exčüą░Ō▒▒ą░te the pot and its contents,ŌĆÖ said Anna Booth, local finds liaison officer.
The story of the excavation will be told in a new BBC Two series, Digging for Britain, which will be broadcast next month.

Treasure hunter Dave Crisp, centre in purple T shirt, oversees the dč¢╔Ī in the field in Frome
-
 Archaeology1m ago
Archaeology1m agoEgyptŌĆÖs StŽģą┐ą┐ią┐g Archaeological Discovery: Alieą┐ Symbols oą┐ Aą┐cieą┐t Coią┐s Spark Extraterrestrial Theories
-

 Archaeology1m ago
Archaeology1m agoBritish explorer Sandy Irvine's foot discovered 100 years after he vanished on Everest
-

 Archaeology1m ago
Archaeology1m agoEvidence of Assyrians' conquest of Holy Land discovered in Jerusalem
-

 Archaeology1m ago
Archaeology1m agoWhy was Stonehenge built?
-

 Archaeology1m ago
Archaeology1m agoWho really wore togas?
-

 Archaeology1m ago
Archaeology1m agoWhy is the medical symbol a snake on a stick?
-

 Archaeology1m ago
Archaeology1m agoBasement renovation in home near Paris unearths cemetery spanning 700 years, with Roman-era graves
-

 Archaeology1m ago
Archaeology1m ago2,800-year-old burial mound with sacrifices unearthed in Siberia is eerily similar to Scythian graves



























