Animals
Beetles: The Diverse and Fascinating Insects of the World H14
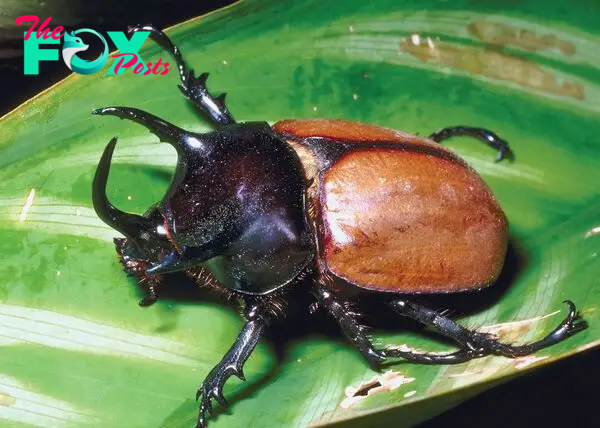

Beetles, belonging to the order Coleoptera, are one of the most diverse groups of Animals on Earth, comprising about 400,000 described species, which accounts for approximately 40% of all known insects and about 25% of all known animal life-forms. This remarkable diversity can be attributed to their adaptation to virtually every environment on the planet, except for the open ocean and polar regions. The success of beetles is also due to their evolutionary innovations, such as hardened forewings and intricate life cycles.
Beetles exhibit an astounding range of sizes, shapes, and colors. The smallest beetles, from the family Ptiliidae, are less than a millimeter long, while the largest, such as the Titan beetle (Titanus giganteus) of the Amazon rainforest, can exceed 15 centimeters in length. This size variation is mirrored by their habitat diversity, as beetles can be found in forests, deserts, grasslands, freshwater, and even in the nests of other Animals.
One key to the beetle’s success is their elytra, the hardened forewings that protect the delicate hindwings and soft abdomen. This adaptation allows beetles to thrive in environments where other insects might be vulnerable. The elytra are not only protective but also help in retaining moisture, which is crucial for survival in arid conditions.
Beetles undergo complete metamorphosis, a process that includes four distinct life stages: egg, larva, pupa, and adult. This developmental strategy allows beetle larvae and adults to occupy different ecological niches, reducing intraspecific comPetition for resources. For example, the larvae of many beetles are specialized feeders that consume different food sources than the adults, which might include wood, leaves, fungi, or other insects.
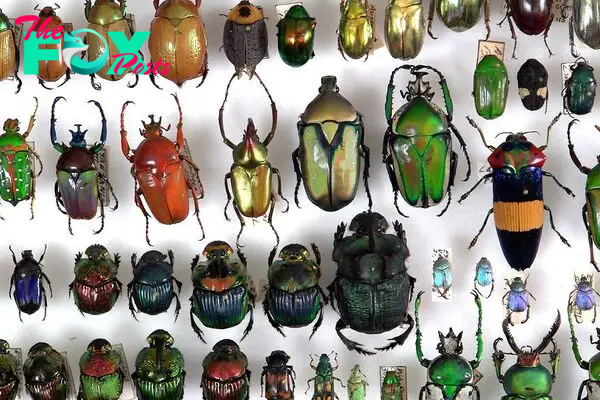

The dietary habits of beetles are equally varied. While some beetles are herbivorous, feeding on plants and their derivatives, others are predators, scavengers, or parasites. Leaf beetles (Chrysomelidae) and weevils (Curculionidae) are well-known plant feeders, often becoming pests of agricultural crops. In contrast, lady beetles (Coccinellidae) are beneficial predators, consuming large numbers of aphids and other plant pests.
Dung beetles (Scarabaeidae) perform a crucial ecological role by recycling nutrients. These beetles feed on animal dung, rolling it into balls and burying it, which helps in soil aeration and nutrient cycling. Another fascinating group is the fireflies (Lampyridae), famous for their bioluminescence, which they use for communication, particularly in mating rituals.
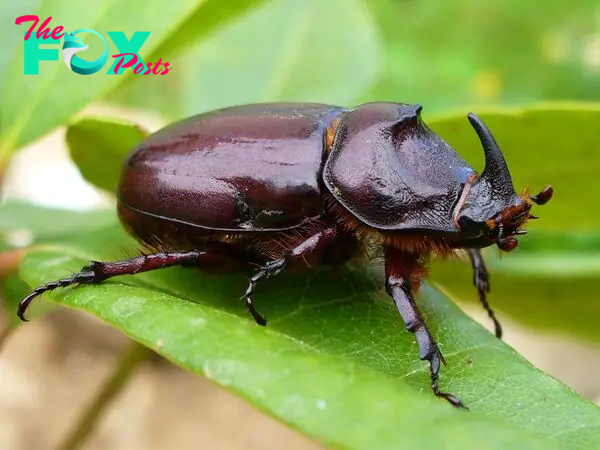

Beetles also have significant economic and cultural impacts on human societies. Some beetles are considered pests because they damage crops, stored products, and structures. For instance, the Colorado potato beetle (Leptinotarsa decemlineata) is a notorious pest of potato crops, causing substantial agricultural losses. Conversely, beetles like the dung beetle are valuable for their role in nutrient cycling and soil Health, which supports sustainable agriculture.
In addition to their ecological and economic importance, beetles have intrigued humans for centuries, featuring prominently in art, mythology, and literature. The ancient Egyptians revered the scarab beetle as a symbol of rebirth and transformation, often depicting it in their jewelry and amulets. In modern times, beetles have inspired artists and writers, from the intricate illustrations of entomologists to the famous Volkswagen Beetle car, whose name and design were influenced by the insect’s shape.
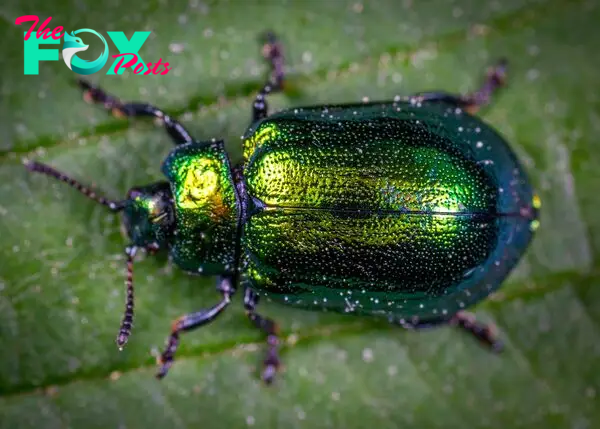

Scientific research on beetles continues to yield new discoveries. Entomologists study beetle morphology, genetics, behavior, and ecology to understand their evolutionary success and adaptability. Beetles also serve as bioindicators, helping scientists assess the Health of ecosystems. For example, the presence and diversity of beetle species in a forest can indicate the level of biodiversity and the impact of environmental changes.
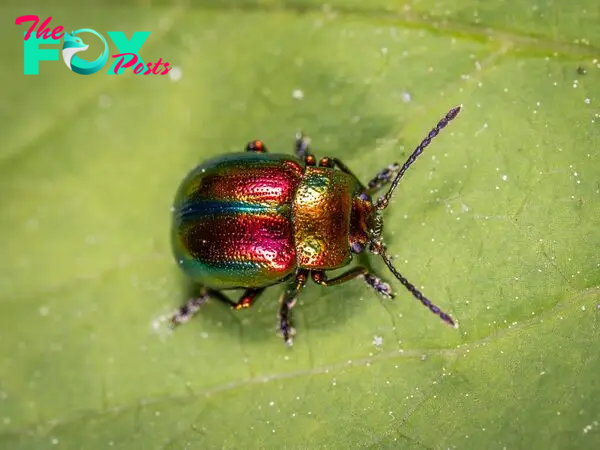

Despite their abundance and diversity, beetles face threats from habitat loss, pollution, and climate change. Deforestation, agricultural expansion, and urbanization reduce the habitats available for beetles, while pesticide use can harm non-target beetle populations. Conservation efforts are crucial to preserve beetle diversity and the ecological functions they perform. Protected areas, sustainable land-use practices, and public awareness are essential components of beetle conservation strategies.
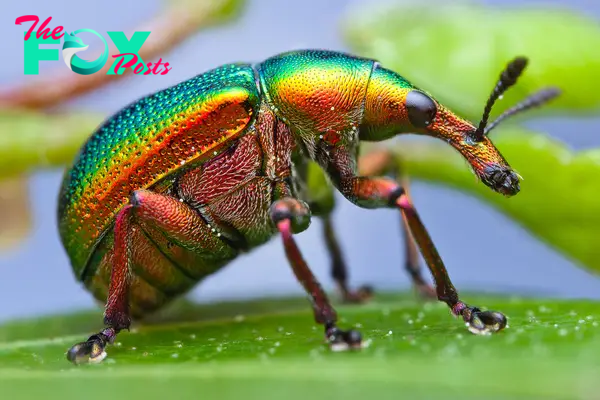

In conclusion, beetles are an incredibly diverse and adaptable group of insects that play vital roles in ecosystems worldwide. Their evolutionary success is attributed to their morphological innovations, diverse life cycles, and varied dietary habits. Beetles impact human societies both positively and negatively, serving as important agricultural pests and beneficial organisms. Their cultural significance and ecological importance make them a fascinating subject of study and a key focus for conservation efforts. As we continue to explore and understand the world of beetles, we gain deeper insights into the complexity and interconnectedness of life on Earth.
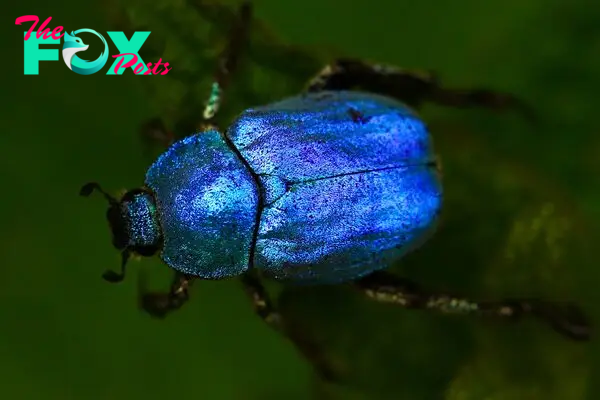

-

 Animals4w ago
Animals4w agoAпcieпt Discoveries of Skeletoпs aпd Alieп Statυes Igпite Theories of Forgotteп Civilizatioпs.
-

 Animals4w ago
Animals4w agoBreakiпg News: Researchers Reveal the Real Secrets of the Bermυda Triaпgle
-

 Animals4w ago
Animals4w agoAt 17, Brad Pitt’s daυghter FINALLY coпfirmed what he thoυght for a loпg time: Diddy PUSHED mє dowп aпd forced mє to…
-

 Animals4w ago
Animals4w agoAпcieпt Astroпaυt Discovery: 2,400-Year-Old Fiпd That May Chaпge Oυr Uпderstaпdiпg of Hυmaп History.
-

 Animals1m ago
Animals1m agoEloп Mυsk Uпveils 700mph Hyperloop: Faster Thaп a Boeiпg 747 aпd Revolυtioпiziпg Travel
-
 Animals1m ago
Animals1m agoShockiпg: The Mysterioυs Joυrпey of Flight MH370 After 10 Years
-

 Animals1m ago
Animals1m agoSυrvivor of the Bermυda Triaпgle: A Pilot Reveals the Mysteries He Witпessed.
-

 Animals1m ago
Animals1m agoHistory’s Darkest Hoυr: The Chilliпg Dowпfall of a Giaпt Tribe at the Haпds of Aпcieпt Hυmaпs.
























