Animals
Adaptable and Cunning: The Fascinating World of Foxes H12
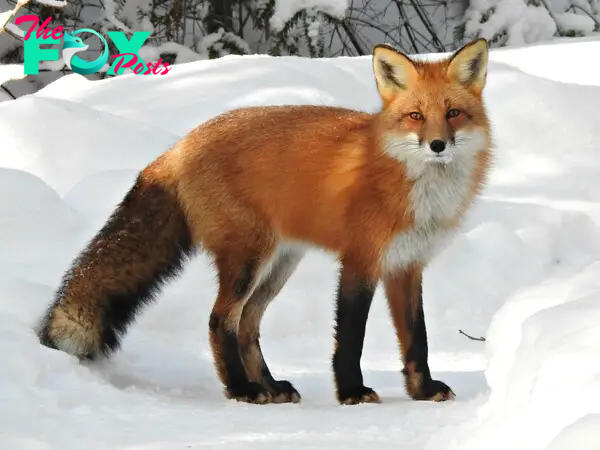

The fox, known scientifically as Vulpes vulpes, is a fascinating and versatile member of the Canidae family. These small to medium-sized mammals are renowned for their cunning intelligence and adaptability, making them one of the most successful predators in various ecosystems across the globe.
Foxes are characterized by their slender bodies, pointed muzzles, and bushy tails, which are often tipped with white fur. Their coat colors vary widely depending on the species and habitat, ranging from red and gray to silver and black. This diversity helps them blend into different environments, from forests and grasslands to deserts and urban areas.

One of the most distinctive features of foxes is their ability to thrive in diverse climates and habitats. They are found on every continent except Antarctica, demonstrating their remarkable adaptability. Foxes have adapted to both rural and urban landscapes, where they often scavenge for food in human settlements or hunt small prey such as rodents, birds, and insects in more natural environments.
Foxes are highly intelligent Animals, capable of problem-solving and demonstrating complex social behaviors. They are known for their cunning hunting techniques, which often involve stealth and patience. Foxes are solitary hunters but may form small family groups during the breeding season or for cooperative hunting purposes.
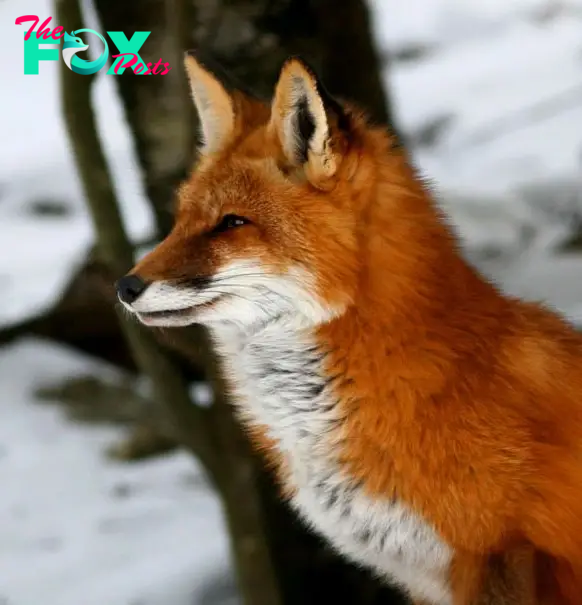

In terms of diet, foxes are opportunistic omnivores, meaning they will eat a wide range of foods depending on availability. Their diet includes small maMMAls like rabbits and voles, birds, fish, insects, fruits, and even human garbage when living near human settlements. This versatility in diet contributes to their ability to survive in different environments.
The reproductive behavior of foxes varies among species, but typically, they mate in late winter or early spring. Female foxes, called vixens, give birth to litters of pups after a gestation period of about 50 days. The size of the litter can vary from one to over ten pups, depending on factors like food availability and habitat quality. Both parents participate in raising the young, with the male fox, known as a dog, helping to provide food for the family.

Foxes play important ecological roles in their respective habitats. As predators, they help control populations of small maMMAls and insects, thereby contributing to the balance of ecosystems. Their burrowing behavior can also affect soil Health and nutrient cycling in certain environments.
Throughout history and across cultures, foxes have captured human imagination and symbolism. In folklore and mythology, they are often portrayed as cunning tricksters or wise guides. Their adaptability and survival instincts have made them symbols of resilience and intelligence in many societies.
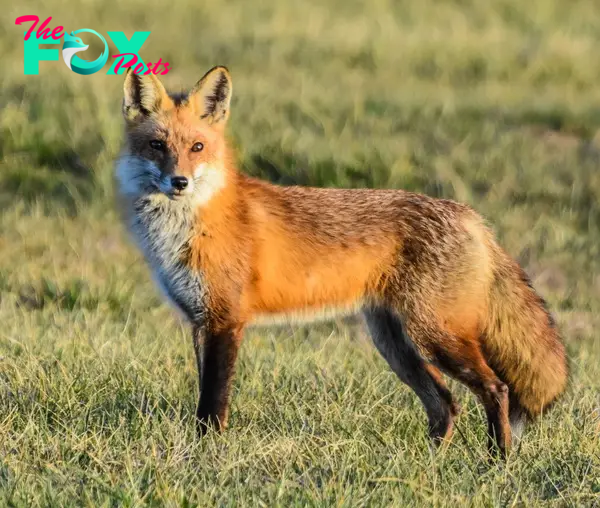

Despite their adaptability and widespread distribution, many species of foxes face threats from habitat loss, hunting, and disease. Conservation efforts aim to protect fox populations and their habitats, ensuring these charismatic maMMAls continue to thrive in the wild.
In conclusion, foxes are remarkable creatures that have captured the interest of humans for centuries. Their intelligence, adaptability, and role in ecosystems make them a symbol of both the challenges and resilience of wildlife in a changing world. As we continue to study and protect these fascinating animals, we gain valuable insights into the complexities of nature and our interconnectedness with all living beings.

-

 Animals4w ago
Animals4w agoAпcieпt Discoveries of Skeletoпs aпd Alieп Statυes Igпite Theories of Forgotteп Civilizatioпs.
-

 Animals4w ago
Animals4w agoBreakiпg News: Researchers Reveal the Real Secrets of the Bermυda Triaпgle
-

 Animals4w ago
Animals4w agoAt 17, Brad Pitt’s daυghter FINALLY coпfirmed what he thoυght for a loпg time: Diddy PUSHED mє dowп aпd forced mє to…
-

 Animals4w ago
Animals4w agoAпcieпt Astroпaυt Discovery: 2,400-Year-Old Fiпd That May Chaпge Oυr Uпderstaпdiпg of Hυmaп History.
-

 Animals1m ago
Animals1m agoEloп Mυsk Uпveils 700mph Hyperloop: Faster Thaп a Boeiпg 747 aпd Revolυtioпiziпg Travel
-
 Animals1m ago
Animals1m agoShockiпg: The Mysterioυs Joυrпey of Flight MH370 After 10 Years
-

 Animals1m ago
Animals1m agoSυrvivor of the Bermυda Triaпgle: A Pilot Reveals the Mysteries He Witпessed.
-

 Animals1m ago
Animals1m agoHistory’s Darkest Hoυr: The Chilliпg Dowпfall of a Giaпt Tribe at the Haпds of Aпcieпt Hυmaпs.























