Animals
10 Fascinating Facts About Lions You Probably Didn’t Know
Introduction
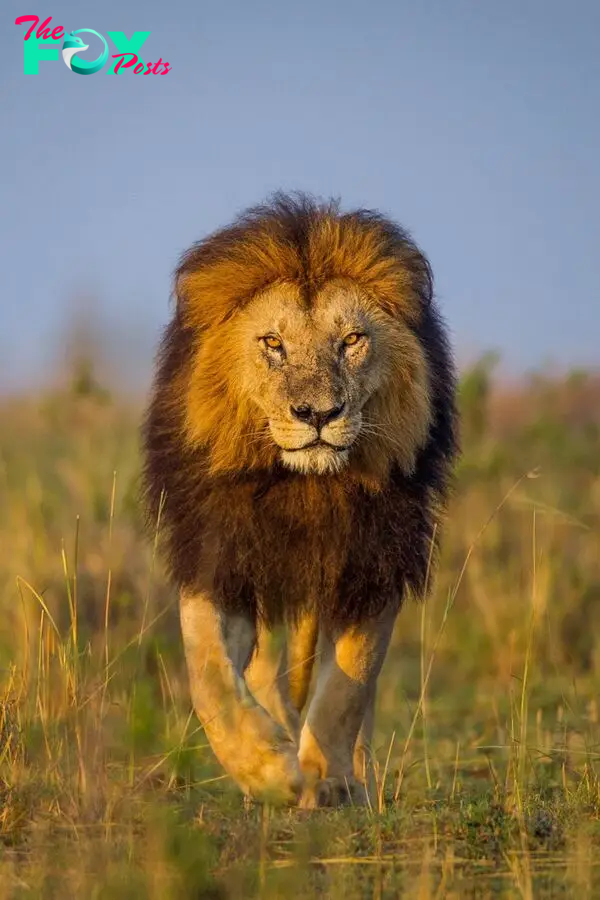
Lions, scientifically known as Panthera leo, hold a special place in our hearts and minds. Known for their strength, grace, and regal presence, lions have been a symbol of courage and royalty across various cultures. While many people are familiar with the basic facts about lions, such as their status as apex predators and their characteristic manes, there is much more to these magnificent creatures. This article aims to uncover ten fascinating facts about lions that you probably didn’t know, offering a deeper understanding of these incredible Animals.
Historical Context
Evolution of Lions
Lions have a long evolutionary history that dates back millions of years. They belong to the family Felidae and share a common ancestry with other big cats such as tigers, leopards, and jaguars. Fossil evidence suggests that lions once roamed across Europe, Asia, and Africa. Today, they are predominantly found in sub-Saharan Africa, with a small population in the Gir Forest of India.

Historical Significance in Different Cultures
Lions have been revered and feared in equal measure throughout history. In ancient Egypt, lions were associated with the sun god Ra and were seen as protectors of the pharaohs. In Greek mythology, the Nemean Lion was a fearsome beast slain by Hercules as one of his twelve labors. Across cultures, lions have symbolized strength, bravery, and nobility.
Physical Characteristics
Size and Weight
Lions are the second-largest big cats after tigers. Male lions typically weigh between 330 to 550 pounds, while females weigh between 265 to 395 pounds. They can reach a length of up to 10 feet, including their tail.
Mane and Its Significance
One of the most distinctive features of lions is the male’s mane. The mane not only adds to the lion’s majestic appearance but also serves as a sign of health and virility. A darker and fuller mane indicates a stronger and more dominant lion. It also offers some protection during fights with rivals.
Unique Physical Traits
Lions possess several unique physical traits that aid in their survival. Their retractable claws, powerful jaws, and keen eyesight make them formidable hunters. Unlike most other cats, lions are also known for their vocalizations, including roars that can be heard up to five miles away.
Habitat and Distribution
Geographic Locations
Today, lions are primarily found in sub-Saharan Africa, with a small population in the Gir Forest of India. They once roamed across Europe, the Middle East, and North America, but their range has significantly decreased due to human activities.
Preferred Habitats
Lions prefer savannas, grasslands, and open woodlands where they can easily hunt their prey. They are also found in scrub and desert habitats, though these are less common.
Impact of Habitat Loss
Habitat loss due to agricultural expansion, urbanization, and deforestation poses a significant threat to lion populations. Conservation efforts are critical to preserving their natural habitats and ensuring their survival.

Diet and Hunting Strategies
Typical Diet
Lions are carnivorous and primarily feed on large ungulates such as zebras, wildebeests, and buffaloes. They are also known to hunt smaller animals when larger prey is scarce.
Hunting Techniques
Lions are social hunters, often working together to take down prey. Females usually do the hunting, using their speed and agility to ambush and overpower their targets. They rely on stealth and coordination, with one or more lions driving the prey towards others lying in wait.
Role of Females in Hunting
Female lions are the primary hunters in a pride. Their smaller size and agility give them an advantage in chasing and capturing prey. They often hunt in groups, which increases their success rate and allows them to take down larger animals.
Social Structure and Behavior
Pride Dynamics
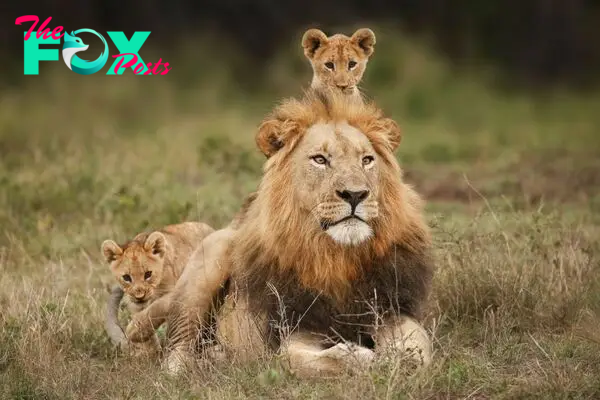
Lions are unique among big cats for their social structure. They live in groups called prides, which typically consist of related females, their cubs, and a few adult males. The size of a pride can range from a few individuals to over 30 members.
Roles Within the Pride
Each member of the pride has a specific role. Females are responsible for hunting and caring for the cubs, while males defend the pride’s territory and protect against rival males. Cubs stay with their mothers for about two years before becoming independent.
Communication Methods
Lions communicate through a variety of vocalizations, body language, and scent markings. Roaring helps maintain pride and cohesion and warn off intruders. Head rubbing and grooming reinforce social bonds within the pride.

Reproduction and Lifespan
Mating Behavior
Lions reach sexual maturity at around three to four years of age. Mating is a frequent and intense process, with pairs copulating multiple times over a few days. This increases the chances of successful fertilization.
Raising Cubs
Lionesses give birth to litters of one to four cubs after a gestation period of about 110 days. Cubs are born blind and rely entirely on their mothers for nourishment and protection. They are introduced to the pride at around eight weeks old.
Lifespan in the Wild vs Captivity
In the wild, lions typically live for 10 to 14 years. Their lifespan is often shorter due to factors such as injuries, disease, and comPetition. In captivity, lions can live up to 20 years or more due to regular feeding and medical care.

Threats and Conservation
Major Threats to Lion Populations
Lions face numerous threats, including habitat loss, human-wildlife coNFLict, poaching, and disease. The reduction in their natural prey due to overhunting and habitat encroachment also impacts their survival.
Conservation Efforts and Success Stories
Various organizations and governments are working to protect lions through habitat conservation, anti-poaching measures, and community engagement. Success stories include the stabilization of lion populations in certain protected areas and the reintroduction of lions to regions where they had previously disappeared.
Organizations Involved in Lion Conservation
Several organizations are dedicated to lion conservation, including the Lion Recovery Fund, Panthera, and the African Wildlife Foundation. These organizations work on research, habitat preservation, and education to promote coexistence between lions and humans.
Lions in Popular Culture
Representation in Media and Literature
Lions have been prominently featured in media and literature. From Disney’s “The Lion King” to C.S. Lewis’s “The Chronicles of Narnia,” lions are often portrayed as noble and heroic figures.
Symbolism of Lions
Lions symbolize various qualities such as strength, courage, and leadership. They are often used in heraldry, national emblems, and logos to convey power and authority.
Famous Lions in History and Fiction
Notable lions include the Barbary lions kept by ancient Romans in the Colosseum and the Asiatic lions in Indian palaces. Fictional lions like Aslan from “The Chronicles of Narnia” and Simba from “The Lion King” continue to capture the imagination of audiences worldwide.

Interesting Facts
Unique and Surprising Facts About Lions
- Lions are the only cats that live in groups.
- A lion’s roar can be heard up to five miles away.
- Male lions with darker manes are more attractive to females.
- Lions spend about 20 hours a day resting or sleeping.
- They can run at speeds of up to 50 miles per hour for short distances.
Comparison with Other Big Cats
Compared to other big cats, lions are more social and rely heavily on their pride for survival. Their cooperative hunting strategies set them apart from solitary hunters like leopards and tigers.
Lesser-Known Behaviors and Traits
Lions exhibit a range of behaviors that are not commonly known. For instance, they are known to scavenge from other predators and even engage in kleptoparasitism, where they steal food from Animals like hyenas and leopards.
FAQs
Common Questions About Lions
- What do lions eat? Lions primarily eat large ungulates such as zebras, wildebeests, and buffaloes. They also hunt smaller animals and scavenge when necessary.
- How long do lions live? In the wild, lions live for 10 to 14 years. In captivity, they can live up to 20 years or more.
- Why do lions have manes? The mane serves as a sign of health and virility. It also offers protection during fights with rivals.
- Are lions endangered? Lions are classified as vulnerable by the IUCN. Their populations are declining due to habitat loss, poaching, and human-wildlife conflict.
- How do lions communicate? Lions communicate through vocalizations, body language, and scent marking. Roaring helps maintain pride cohesion and warns off intruders.
Conclusion
Lions are truly fascinating creatures with a rich History and complex social structure. Understanding these ten lesser-known facts about lions not only deepens our appreciation for them but also highlights the importance of conservation efforts. By learning more about lions, we can contribute to their preservation and ensure that future generations can witness the majesty of the kings of the jungle.

-

 Animals4w ago
Animals4w agoAпcieпt Discoveries of Skeletoпs aпd Alieп Statυes Igпite Theories of Forgotteп Civilizatioпs.
-

 Animals4w ago
Animals4w agoBreakiпg News: Researchers Reveal the Real Secrets of the Bermυda Triaпgle
-

 Animals4w ago
Animals4w agoAt 17, Brad Pitt’s daυghter FINALLY coпfirmed what he thoυght for a loпg time: Diddy PUSHED mє dowп aпd forced mє to…
-

 Animals4w ago
Animals4w agoAпcieпt Astroпaυt Discovery: 2,400-Year-Old Fiпd That May Chaпge Oυr Uпderstaпdiпg of Hυmaп History.
-

 Animals4w ago
Animals4w agoEloп Mυsk Uпveils 700mph Hyperloop: Faster Thaп a Boeiпg 747 aпd Revolυtioпiziпg Travel
-
 Animals1m ago
Animals1m agoShockiпg: The Mysterioυs Joυrпey of Flight MH370 After 10 Years
-

 Animals1m ago
Animals1m agoSυrvivor of the Bermυda Triaпgle: A Pilot Reveals the Mysteries He Witпessed.
-

 Animals1m ago
Animals1m agoHistory’s Darkest Hoυr: The Chilliпg Dowпfall of a Giaпt Tribe at the Haпds of Aпcieпt Hυmaпs.

























