Science
Astronomers spot a possible 'future Earth' — 8 billion years into its future
Astronomers have discovered a distant planet that has offered them a rare glimpse of what our planet may look like 8 billion years in the future.
The planet, called KMT-2020-BLG-0414 and located 4,000 light-years from Earth, is a rocky world orbiting a white dwarf — the embering husk of a star. Our sun is expected to transform into a white dwarf in 5 billion years’ time.
Before that, though, our sun will first accelerate outward into a red giant, consuming Mercury, Venus, and possibly even Earth and Mars. If our planet is spared, it could eventually resemble this one, drifting farther out from the cooling remains of the dying cosmic furnace. The researchers described the distant world Sept. 26 in the journal Nature Astronomy.
"We do not currently have a consensus whether Earth could avoid being engulfed by the red giant sun in 6 billion years," lead author Keming Zhang, an astronomer at University of California San Diego, said in a statement. "In any case, planet Earth will only be habitable for around another billion years, at which point Earth's oceans would be vaporized by runaway greenhouse effect — long before the risk of getting swallowed by the red giant."
For most of their lives, stars burn by fusing hydrogen into helium. Once they have exhausted their hydrogen fuel, however, they begin fusing helium, leading to a massive increase in energy output that causes them to swell to hundreds or even thousands of times their original size — and gobbling up any nearby planets as they transform into red giants.
Related: Scientists may finally understand why large alien planets keep turning into 'super-Earths'
The remote planetary system is located near the bulge at the center of our Milky Way galaxy, and was first noticed by astronomers in 2020 when it moved in front of the light of an even more distant star located 25,000 light years away. As gravity warps space, the system warped the far-away star’s light, acting as a ‘gravitational lens’ and making its presence detectable.
-

 Science1d ago
Science1d agoThe 5-Minute Game That Will Improve Your Relationship With Your Dog
-

 Science2d ago
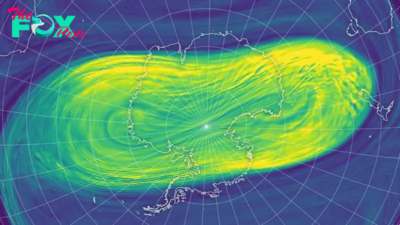
Science2d agoEarth from space: Iconic 'Star Trek' symbol shines brightly in sea of muddy Arctic sea ice
-

 Science2d ago
Science2d agoWeird 'zebra rock' on Mars is unlike anything seen before on Red Planet, NASA says
-

 Science2d ago
Science2d agoA 'primordial' black hole may zoom through our solar system every decade
-

 Science2d ago
Science2d agoMysterious, ultraheavy stars are gobbling up atmospheres like carrion, new study hints
-

 Science2d ago
Science2d agoBright comet Tsuchinshan-ATLAS could be visible without a telescope for the 1st time in 80,000 years. Here's how to see it this week.
-
 Science3d ago
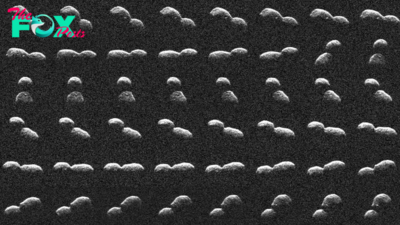
Science3d agoNASA reveals images of enormous, snowman-shaped asteroid 2024 ON after its ultra-close approach to Earth
-
 Science3d ago
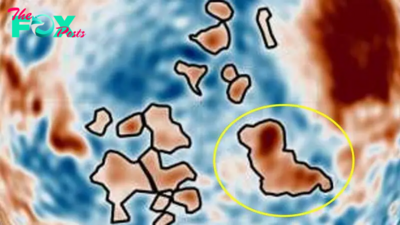
Science3d ago'Martian dog' and dozens of other mysterious blobs found hiding under Mars' north pole in new 'gravity map'